Physical Activity & Technology
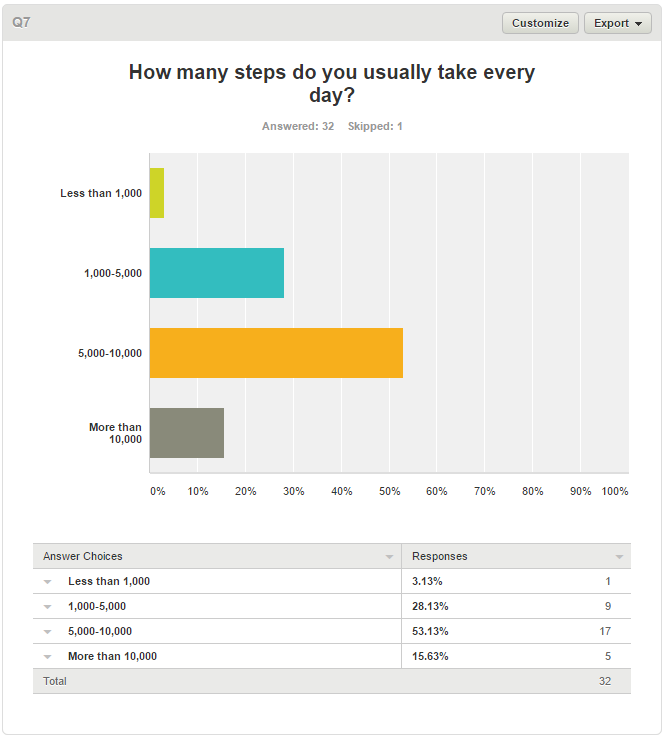
Debated by many, the question “What is the single best thing we can do for our health” yields numerous answers. Dietitians argue it’s our daily diets, fitness professionals argue it’s our lack of daily activity, and US media say it’s increasing coffee consumption or was it increasing chocolate consumption. Regardless, the only thing everyone can agree on is no one can agree on one particular “single best thing.” A doctor-professor at the Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute believes it’s limiting our sedentary activity to 23 and ½ hours a day. According to Dr. Mike Evans, just 30 minutes of exercise throughout the day leads to a large health benefits. Another simple way to improve our health is to take 10,000 steps a day according to the American Heart Association. Studies show it can increase a person’s energy, reduce risk for Type II diabetes, and reduce risk for heart disease. With these 2 simple lifestyle changes, we decided to look into how to incorporate these changes into our daily lives.
The addition of physical activity might not be the single best thing we can do for our health, but some might say it is the simplest thing we can do for our health. According to the CDC, some of the benefits associated with regular physical activity includes:
- Weight control
- Reduced cardiovascular disease risk
- Reduced risk for type II diabetes and/or metabolic syndrome
- Reduced risk for some cancers
- Improved mental health and/or mood
- Improved ability and energy to do daily activities
- Increased fall prevention in geriatric population
- Increased life expectancy
- Improved cardiovascular health
- Decreased risk for high blood pressure
- Improved bone and muscle strength
These benefits are seen with 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity a week. Additionally, increased benefits are seen with 300 minutes and 150 minutes of moderate and vigorous intensity, respectively, aerobic activity a week.
Recently there’s been a rising popularity in activity related technology. With the introduction of smartphones fitness trackers, wearable tech fitness trackers (Fitbit, Garmin, etc...), and exergaming (exercise related video games), exercising has appealed to a wider range of people. One of the many discouraging factors limiting the engagement in physical activity is enjoyment. Not everyone enjoys running miles, lifting weights, or playing a sport. The addition of technology opens up the world of exercising to the masses


Wearable Techs
One of the more popular gadgets the majority has adopted are “wearables.” These are gadgets are primarily watches or bands that is able to:
- Track daily steps
- Track heart rate
- Use GPS to track running distance and map running routes
- Calculate burned calories
- Track sleeping patterns
- Track exercises and workout time
Wearables are marketable to a wide variety of people based on what features you want. For the simple user, there are plenty of step trackers that keep time and track your daily steps. For the more serious weekender, companies like Garmin and Fitbit boast more fully loaded watches that can provide trackers to improve your workout routine. With these more serious wearables, you can partake in more specified workouts such as heart rate based training, time sensitive workouts, or distance based workouts. According to a review by Harvard Health Publication, a small study shows that a group of overweight postmenopausal women increased their weekly physical activity by an additional 38 minutes compared to a group using basic pedometers.
Smartphones and Apps
With smartphones becoming a common item the average person carries on a daily basis, health companies started utilizing them to make phones more marketable. Samsung and Apple is in the forefront for healthy applications (apps) with the implementation of a step counter, heart rate monitor, and GPS mapping service built in their phones. Other 3rd party apps exist for download that offer a wide range of services that appeal to those who are at the start of their exercise journey or to the experienced who is training for that 5th marathon. Applications such as MyFitnessPal offers daily calorie tracking, workout recommendations, workout tracking, weight loss tracking, and various other useful tools to guide novices through their lifestyle changes or assist the knowledgeable in fine tuning their workouts.


Exergaming
Video games have mainly involves sitting for long periods of time and watching a screen. Within the last decade, gaming companies have pushed the idea of gaming involving the player’s body as a control. It started with Nintendo’s Wii console utilization of motion controlled games that allowed controllers that require the use of hand movement. Games such as Wii Sports and Wii Fit added an aerobic exercise component to video games that increased daily activity participation. According to a review of multiple studies published in the Journal of Physical Activity & Health, it was found that Wii Fit games and Wii Sports games required an energy expenditure equivalent to moderate-intensity workout.
As the Wii’s popularity increased, other companies with a market share in the gaming market introduced their own exergaming products. Microsoft came out with the Kinect allowing their gaming console, the Xbox, to play motion capture games. The Xbox Kinect differentiated itself from the Wii, with its use of the player’s full body as a controller. A popular game played on the Kinect is Dance Central. The player must replicate the dance moves showed on the screen to score points. Dancing is not only a great way to burn calories, but it makes exercising fun.
Augmented Reality
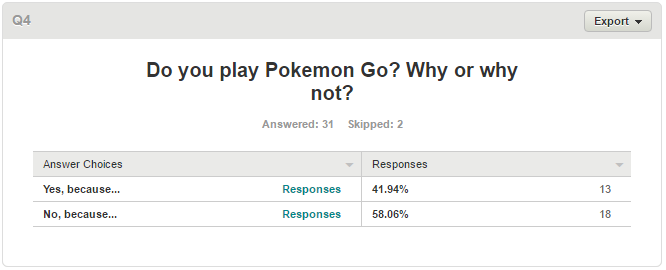
The latest in exergaming is augmented reality (AR). AR is essentially the real-world environment are supplemented by computer-generation. A game that has recently gained the spotlight is Nintendo’s PokemonGo. It’s a game that essentially requires the player to roam outside to perform various tasks in the game. Tasks such as hatching an egg is a distance specific task that requires the player to log in a certain distance while playing the game. The main point of the game is to catch various pokemon scattered throughout the real-world environment thus forcing the players to walk around in parks, neighborhoods, and/or cities. The game masks the feeling of work associated with walking long distances by adding goal oriented tasks.
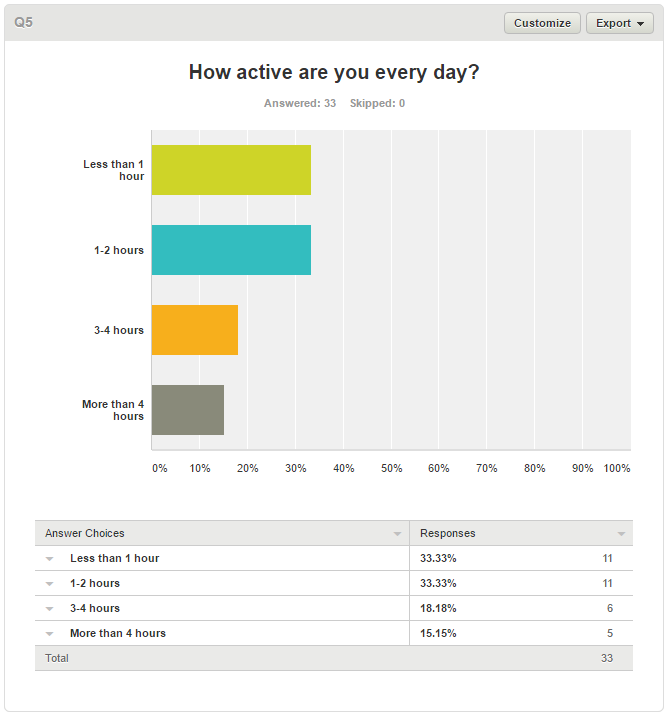
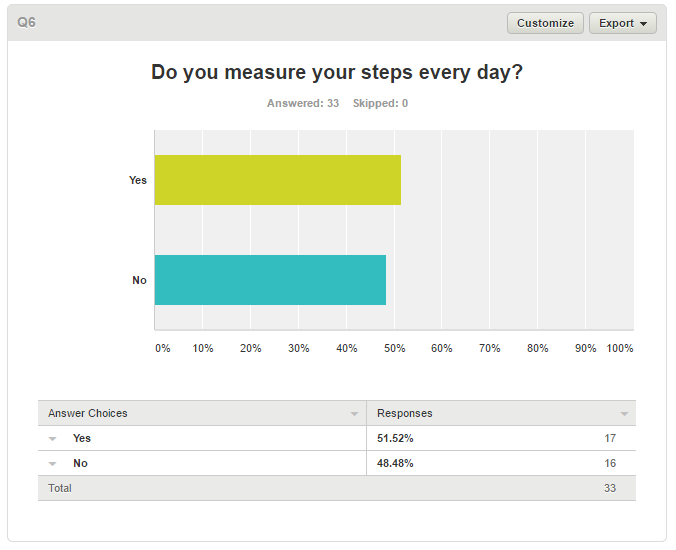
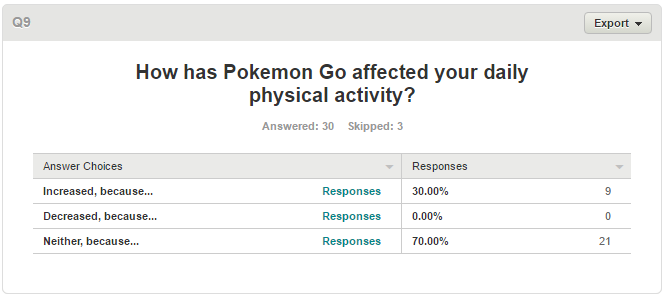
Pokemon Go Survey
Virtual Reality
With technology allowing developers and manufacturers to shrink the size of products without sacrificing their capabilities, we are slowly gaining the ability to live in a virtual world. Virtual reality (VR) is able to immerse users in a computer generated environment with the addition to artificially recreate sensory experience. A company called Zero Latency is in the forefront of VR gaming that changes the entire gaming environment. Instead of having to sit and watch a screen, it forces users to perform the actions they want replicated in the virtual world. It adds an activity aspect to gaming that the industry lacks currently.
References
23 and 1/2 hours: What is the single best thing we can do for our health? [Video file]. Retrieved from http://www.evanshealthlab.com/23-and-12-hours/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2015). Physical Activity and Health Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/physicalactivity/basics/pa-health/
D Tausig. (2012, Jan 26). 23 and 1/2 hours –- What is the best Thing We Can Do for Our Health? [Web log comment]. Retrieved from http://www.sparkpeople.com/blog/blog.asp?post=video_23_and_12_hours_what_is_the_single_best_thing_we_can_do_for_our_health
H Godman. (2015, Aug 27). Can Digital fitness trackers get you moving? [Web log comment]. Retrieved from http://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/can-digital-fitness-trackers-get-you-moving-201508278214
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2016). Benefits of Physical Activity. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/phys/benefits
Sween, J., Wallington, S. F., Sheppard, V., Taylor, T., Llanos, A. A., & Adams-Campbell, L. L. (2014). The Role of Exergaming in Improving Physical Activity: A Review. Journal of Physical Activity & Health, 11(4), 864–870. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4180490/
Zero Latency VR – Survival Trailer [Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.zerolatencyvr.com/